MiCOR Data Team
Areas of Influence
The mission of the Military Cardiovascular Outcomes Research (MiCOR) program is to enhance the cardiovascular health and well-being of the Warfighter and the DoD community through innovative clinical research using precision techniques. The data team is critical to accomplishing this mission, applying cutting edge machine learning techniques to a wide array of datasets/applications. Modeling techniques utilized by the data team include, but are not limited to: statistical inference including linear and non-linear models, machine learning tools such as tree-based methods, clustering algorithms, PCA, and SVMs, time series forecasting including matrix profiles, signal analysis using fast Fourier transforms, model-agnostic explanatory analysis using SHAP values, and neural network architectures including MLP’s and LLM’s.
The primary mission of the MiCOR data team is to provide statistically proven, explainable models to the MiCOR investigators and collaborating investigators to aid in the execution and assessment of clinical research projects.
Representative Ongoing Projects
-
COVIVA - Comparative Cohort Study of Post-Acute COVID-19 Infection with a Nested, Randomized Controlled Trial of Ivabradine for those with Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (collaboration with award # HU00012120090)
-
Prospective, comparative observation of 200 evaluable subjects with Long Haul COVID enriched for those with features suggesting autonomic dysfunction. Of those 200 in the observational cohort, 50 participants with POTS will be identified for the RCT.
-
Continuous ECG, ambulatory blood pressure, proteomics and genomics
-
The RCT evaluates the impact of Ivabradine on reducing heart rate and controlling symptoms.
-
Data team to explore role of sympathetic nervous system activation in LHC
-
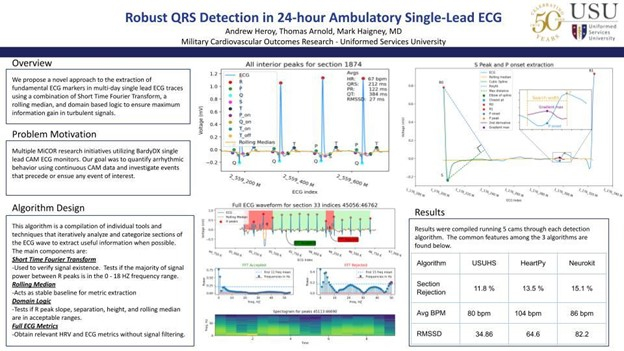
● Electrocardiographic Detector
- Novel open-sourced approach to identifying salient features and measurements in very long ambulatory ECG recordings in humans. Instead of using signal to noise ratio (SNR) to establish loss of signal in noisy ECG’s, we implement a Fast Fourier Transform to search for standard QRS frequencies and historical data (within the ECG) to validate / extract desirable features from the ECG signal.
- Features extracted include: PQRST Peaks, onset/offset PQT peaks, HR, HRV, RMSSD, NN50, PNN50.
- Open source repo for Robust Agile Detector (RAD_ECG) https://github.com/METIS-MICOR/rad_ecg
-
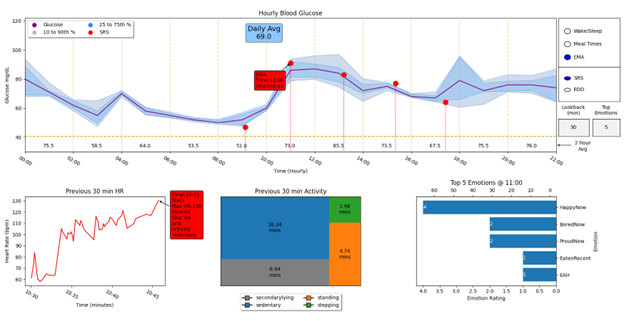
ASSET: Addressing Anxiety and StreSs for Healthier Eating in Teens
-
A multisite, randomized controlled pilot and feasibility trial
-
Study recruited adolescent girls who are at risk for adult obesity or cardiometabolic disease with elevated anxiety symptoms will be enrolled between two sites (USU and Colorado State University); N=40
-
Continuous ECG, blood glucose, activity and mood measurements to permit multimodal evaluation of the role of sympathetic nervous system activation and binge eating
-
Participants randomized to a 12-session IPT or CBT group program, and followed for up to 3 years
-
-
USAFE- US Air Force ECG Project
-
Big data analysis of nearly 1,000,000 electrocardiograms performed by the US Air Force
-
Use machine learning techniques to identify the electrocardiographic features that are most predictive of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes
-
Develop new algorithms based on “C” to screen ADSM for asymptomatic heart disease that impairs readiness
-
-
SPIRIT- Sleep, HypertensIon, and Cardiovascular Disease in Injured Veterans
-
A prospective, cross-sectional study of two groups of participants (100 participants per group) who were injured in combat, enrolled in the WWRP and have previously agreed to be contacted for future research.
-
This study further investigates the accumulating evidence suggesting that SNS activation may underlie HTN and be bidirectionally impacted by sleep disorders, we propose to study the association of sleep disorders with electrocardiographic measures and their impact on the risk for increased blood pressure.
-